If you are planning to buy a new inverter for your home or you need to upgrade your old one, it’s important that you understand how to choose the right inverter. Don’t confuse power rating requirement of your home with that of your neighbor. It doesn’t work that way. Don’t go about installing the same inverter in your home just because of power rating only. You need to do a little background research to discover what works for you.

To help you find the right inverter here are 5 important things you need to know;
1. Power requirements
Calculate your power requirements in watts to find a suitable inverter that fits your needs. Inverters are very precise equipment that can get damaged if overloaded, so determine the total watts that all appliances will need before purchasing a reliable inverter.
Let’s take a hypothetical situation; suppose you want to run 3 fans, 4 light bulbs and 2 television sets at the same time. Find below the average power consumed by each of these appliances:
1 Fan – 70 watts
1 light bulb – 60 watts
1 Television set – 120 watts
Your power requirements will be (3 x 70) + (4 x 60) + (2 x 120) = 690 watts
2. VA Rating
It’s important that you understand the VA rating of the inverter you chose to buy because it represents the voltage and current supplied by the inverter. In the hypothetical situation that you find an inverter that operates at 100% efficiency, it means the power supplied by the inverter to those required by the appliances are the same. Practically speaking, no inverter works at 100% efficiency. Most fall within 60-80% efficiency. In fact think about pure sine wave inverter if you need high efficiencies.
The efficacy is the ratio of power required by appliances to power supplied by the inverter. This efficiency is known as power factor and ranges between 0.6 to 0.8
Hence power supplied = Power requirement /Power factor
If an inverter has a power factor of 0.7 then the required watts needed to tackle our hypothetical total watts of 690 should be
Power of inverter (VA) = 690/0.7 = 985 VA
3. Get to know the battery your inverter needs
The performance and lifespan of the battery is the reason why it is regarded as the backbone of any inverter system. Battery quality is important so it’s wise if you understood the intricate designs and capabilities of the battery. The capacity of your battery will determine how long your inverter will last. It is the batteries that determine back up powers.
Battery capacities come in Ah and it’s commonplace to find 100, 150 or 180Ah capacity batteries.
Back to our hypothetical total watts of 690, if you want the inverter to run for 3 hours, here is a simple calculation to determine the battery capacity to buy.
*Using a 12V battery
Battery capacity = total watts x back up hours needed(3 hours) /battery volts
Battery capacity = 690 x 3/12 = 172.5 Ah
From the calculations, you will need a battery capacity of about 180Ah to provide 3 hours of backup electricity to a total watt requirement of 690.
4. What appliances can be powered by inverters?
Although fridges and air conditioners can be powered by inverters, these equipment utilize compressors that need huge amounts of currents before they starting up. Once they are ruining, the current is then stabilized to normal levels. To use an inverter with these appliances, you will need to buy an inverter that has a high VA value or go for specialized inverters dedicated for compressor appliances.
5. Warranty Period
To make the most out of your investment dollar ensure that the inverter you buy should come with a strong warranty period. Inverters are quite expensive to purchase with pure sine waves reaching as high as $2,500. So don’t gamble your hard-earned money on what isn’t built to last.
Inverters require little to no maintenance as long as the environment where it operates is conducive for it. Make sure you buy from reputable manufacturers who give correct details about their products.
Lastly, don’t be fooled by cheap knock-off inverters branded as pure sine waves when all they offer is a modified sine wave or even a square sine wave.
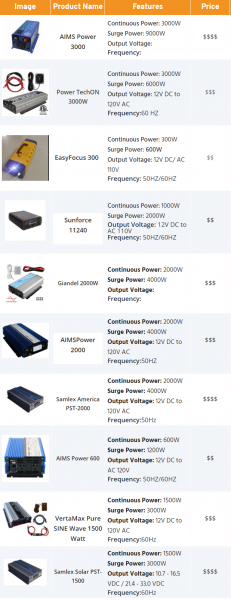
Gladly, we have compiled this awesome comparison table that will allow you to make a purchase decision fast.